|
|
Laying Out Components within a Container |
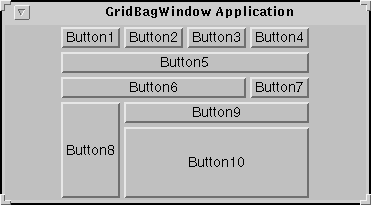
Here, again, is the applet that shows a GridBagLayout in action.
Below is the code that creates the GridBagLayout and the components it manages. (Here's the whole program. The program runs either within an applet, with the help of AppletButton, or as an application.)
protected void makebutton(String name, GridBagLayout gridbag, GridBagConstraints c) { Button button = new Button(name); gridbag.setConstraints(button, c); add(button); } public GridBagWindow() { GridBagLayout gridbag = new GridBagLayout(); GridBagConstraints c = new GridBagConstraints(); setFont(new Font("Helvetica", Font.PLAIN, 14)); setLayout(gridbag); c.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH; c.weightx = 1.0; makebutton("Button1", gridbag, c); makebutton("Button2", gridbag, c); makebutton("Button3", gridbag, c); c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row makebutton("Button4", gridbag, c); c.weightx = 0.0; //reset to the default makebutton("Button5", gridbag, c); //another row c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE; //next-to-last in row makebutton("Button6", gridbag, c); c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row makebutton("Button7", gridbag, c); c.gridwidth = 1; //reset to the default c.gridheight = 2; c.weighty = 1.0; makebutton("Button8", gridbag, c); c.weighty = 0.0; //reset to the default c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row c.gridheight = 1; //reset to the default makebutton("Button9", gridbag, c); makebutton("Button10", gridbag, c); }This example uses one GridBagConstraints instance for all the components the GridBagLayout manages. Just before each component is added to the container, the code sets (or resets to default values) the appropriate instance variables in the GridBagConstraints object. It then uses the
setConstraints()method to record all the constraint values for that component.For example, just before adding a component that ends a row, you'll see the following code:
And just before adding the next component (if the next component doesn't take up a whole row), you'll see the same instance variable reset to its default value:c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end rowFor clarity, here's a table that shows all the constraints for each component the GridBagLayout handles. Values that aren't the default are marked in bold font. Values that are different from those in the previous table entry are marked in italic font.c.gridwidth = 1; //reset to the defaultComponent Constraints --------- ----------- All components gridx = 0, gridy = 0 fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH ipadx = 0, ipady = 0 insets = new Insets(0,0,0,0) anchor = GridBagConstraints.CENTER Button1, Button2, Button3 gridwidth = 1 gridheight = 1 weightx = 1.0 weighty = 0.0 Button4 gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER gridheight = 1 weightx = 1.0 weighty = 0.0 Button5 gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER gridheight = 1 weightx = 0.0 weighty = 0.0 Button6 gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE gridheight = 1 weightx = 0.0 weighty = 0.0 Button7 gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER gridheight = 1 weightx = 0.0 weighty = 0.0 Button8 gridwidth = 1 gridheight = 2 weightx = 0.0 weighty = 1.0 Button9, Button10 gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER gridheight = 1 weightx = 0.0 weighty = 0.0All the components in this container are as large as possible, given their row and column. The program accomplishes this by setting the GridBagConstraints
fillinstance variable toGridBagConstraints.BOTH, leaving it at that setting for all the components. If the program didn't specify the fill, the buttons would be at their natural size, like this:

This program has four components that span multiple columns (Button5, Button6, Button9, and Button10) and one that spans multiple rows (Button8). In only one case (Button8) is the height or width of the component explicitly specified. In all the other cases, the width of the component is specified as either
GridBagConstraints.RELATIVEorGridBagConstraints.REMAINDER, which lets the GridBagLayout determine the component's size, taking into account the size of other components in the row.When you enlarge the window the program brings up, you'll notice that the columns stay equal in width as they grow. This is the result of each component in the first row (where each component is one column wide) having
weightx = 1.0. The actual value of these components'weightxis unimportant. What matters is that all the components (and thus all the columns) have an equal weight that is greater than 0. If no component managed by the GridBagLayout hadweightxset, then when the components' container was made wider, the components would stay clumped together in the center of the container, like this:
Another thing you'll notice as you enlarge the window is that the last row is the only one that gets taller. This is because only Button8 has
weightygreater than zero. Button8 spans two rows, and the GridBagLayout happens to allocate all Button8's weight to the bottom-most row Button8 occupies.
|
|
Laying Out Components within a Container |