WordNet is a semantic lexicon for the English language that is used extensively by computational linguists and cognitive scientists. WordNet groups words into sets of synonyms called synsets and describes semantic relationships between them. One such relationship is the is-a relationship, which connects a hyponym (more specific synset) to a hypernym (more general synset). For example, a plant organ is a hypernym to plant root and plant root is a hypernym to carrot.
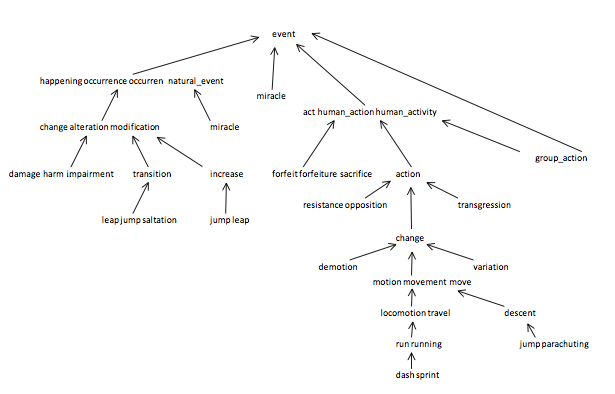
The WordNet DAG. Your first task is to build the WordNet graph: each vertex v is an integer that represents a synset, and each directed edge v→w represents that w is a hypernym of v. The graph is directed and acyclic (a DAG), though not necessarily a tree since a synset can have several hypernyms. A small subgraph of the WordNet graph is illustrated below.

We now describe the two data files that you will use to create the WordNet digraph. The files are in CSV format: each line contains a sequence of fields, separated by commas.
means that the synonym set whose elements are AND_circuit and AND_gate has an id number of 45, and it's gloss is a circuit in a computer that fires only when all of its inputs fire. The individual nouns that comprise a synset are separated by spaces (and a synset element is not permitted to contain a space).45,AND_circuit AND_gate,a circuit in a computer that fires only when all of its inputs fire
171,22798,57458
means that the the synset 171 ("Actifed") has 2 hypernyms: 22798 ("antihistamine") and 57458 ("nasal_decongestant"), representing that Actifed is both an antihistamine and a nasal decongestant. The synsets are obtained from the corresponding lines in the file synsets.txt.
171,Actifed,trade name for a drug containing an antihistamine and a decongestant... 22798,antihistamine,a medicine used to treat allergies... 57458,nasal_decongestant,a decongestant that provides temporary relief of nasal...
Efficiently implement an immutable data type WordNet with the following API:
// constructor takes the name of the two input files public WordNet(String synsets, String hypernyms) // return all of the glosses associated with a given noun's synsets public Iterable<String> glosses(String noun) // is the word a WordNet noun? public boolean isNoun(String word) // return the distance between nounA and nounB (defined below); -1 if infinite public int distance(String nounA, String nounB) // return the synset (second field of synsets.txt) that is the common ancestor // of nounA and nounB in a shortest ancestral path; null if no such path (defined below) public String sap(String nounA, String nounB)
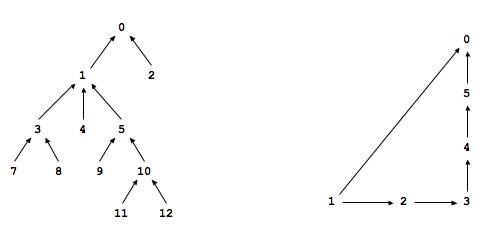
Shortest ancestral path. An ancestral path between two vertices v and w in a digraph is a directed path from v to a common ancestor x, together with a directed path from w to the same ancestor x. A shortest ancestral path is an ancestral path of minimum total length. For example, in the digraph at left, the shortest ancestral path between 3 and 11 has length 4 (with common ancestor 1). In the digraph at right, one ancestral path between 1 and 5 has length 4 (with common ancestor 5), but the shortest ancestral path has length 2 (with common ancestor 0).
Implement an immutable data type SAP with the following API:
Also, include a main() that takes the name of a digraph input file (standard format used by Digraph) as a command-line argument, constructs the digraph, reads in vertex pairs from standard input (for illustration purposes, the text that you type is shown in bold), and prints out the length of the shortest ancestral path between the two vertices and a common ancestor that participates in that path.// constructor public SAP(Digraph G) // return length of shortest ancestral path of v and w; -1 if no such path public int length(int v, int w) // return a common ancestor of v and w that participates in a shortest ancestral path; -1 if no such path public int ancestor(int v, int w)