An Example
The following details the way that I like to use sml and emacs. Feel free to
ignore it, but it's a good place to start if you're completely confused.
If you've got an Xserver such as Exceed running, type
emacs foo.sml &. If not, you can do
emacs -nw foo.sml. (In this case, you'll get
grayscale syntax highlighting.)
Assuming you are using the provided
.emacs
file, emacs will realize from the file extension that you are writing sml code
and automatically put you into sml mode. You'll see
(SML)
on the dark bar near the bottom of the window. You'll also get an SML menu on
the top bar.


Emacs has slightly odd notions of windows. A emacs frame is basically what you
usually think of as a window. You can divide a frame into multiple windows
(just like splitting the screen in most editors). A buffer is an open file or
some other process (such as the SML buffer or the default scratch buffer). So
for example, you can have one frame split into two windows, while having three
files open, two of which are visible at the moment.
I use the following keyboard shortcuts to set up my workspace the way I like
it. (The same options should be available in the menus somewhere.)
C-x
means hit
Control
and
x
at the same time.
M-xmeans hit
Alt
or
Esc
and
x. (Note that if you're using an Xserver, you may
have to set it up to forward
Alt
to X.)
C-x b
means hit
Control
and
x
at the same time and then hit
b.
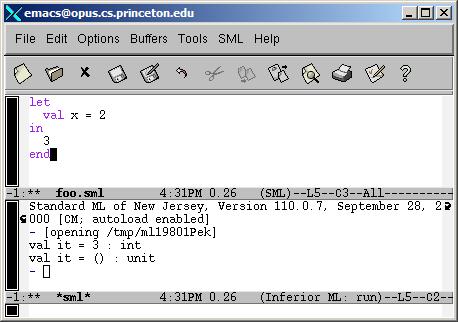
- C-x 2 divides the frame horizontally into two windows.
- C-x o moves you to the other window.
- M-x sml enter starts SML in the background.
- C-x b *sml* enter switches buffers and moves SML into the lower window.
- C-x o moves you back to the top window.
- C-c C-b loads the current buffer into SML and the results will be displayed in the SML process in the bottom window.

If emacs gets confused while you are entering a command, hitting
C-g
a few time usually sorts things out. If you're typing words (like a file name
or buffer name), you can use tab-completion.
Here are a few more useful emacs commands.
